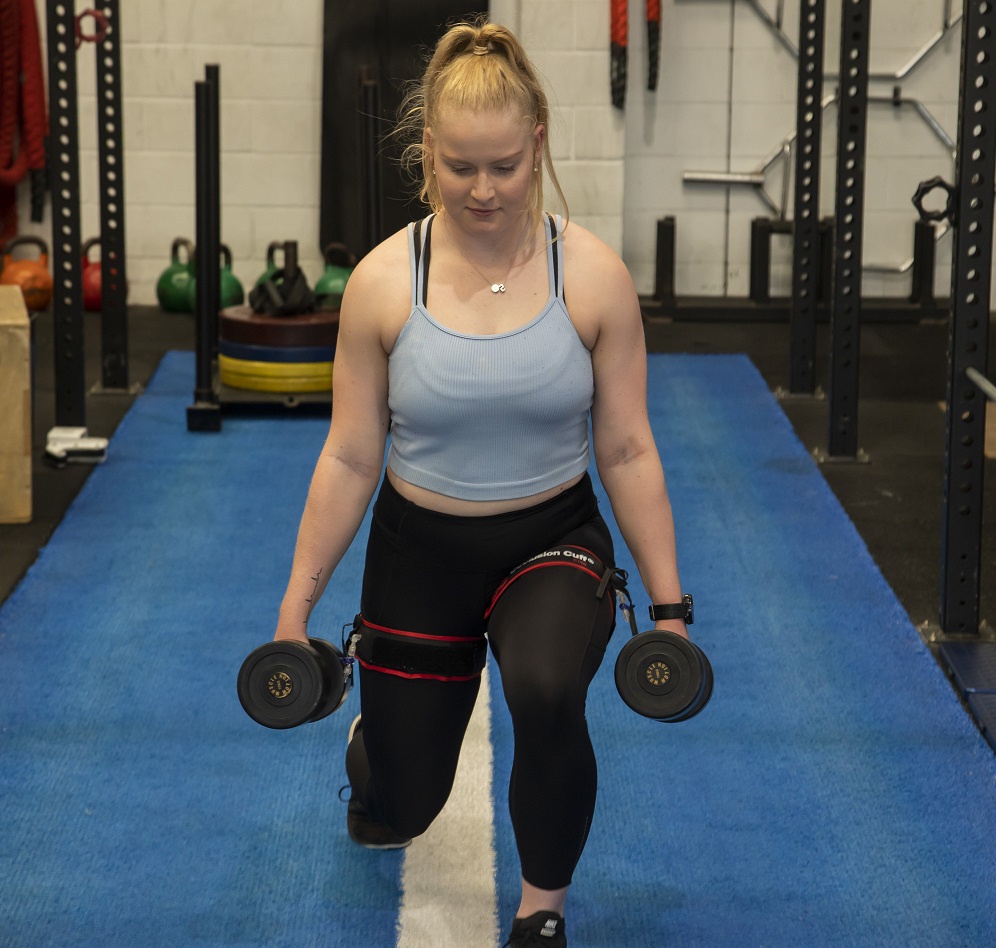
When it comes to improving physical health and recovering from injuries, two fields play crucial roles: exercise physiology and physiotherapy. These disciplines offer unique approaches to enhance overall well-being.
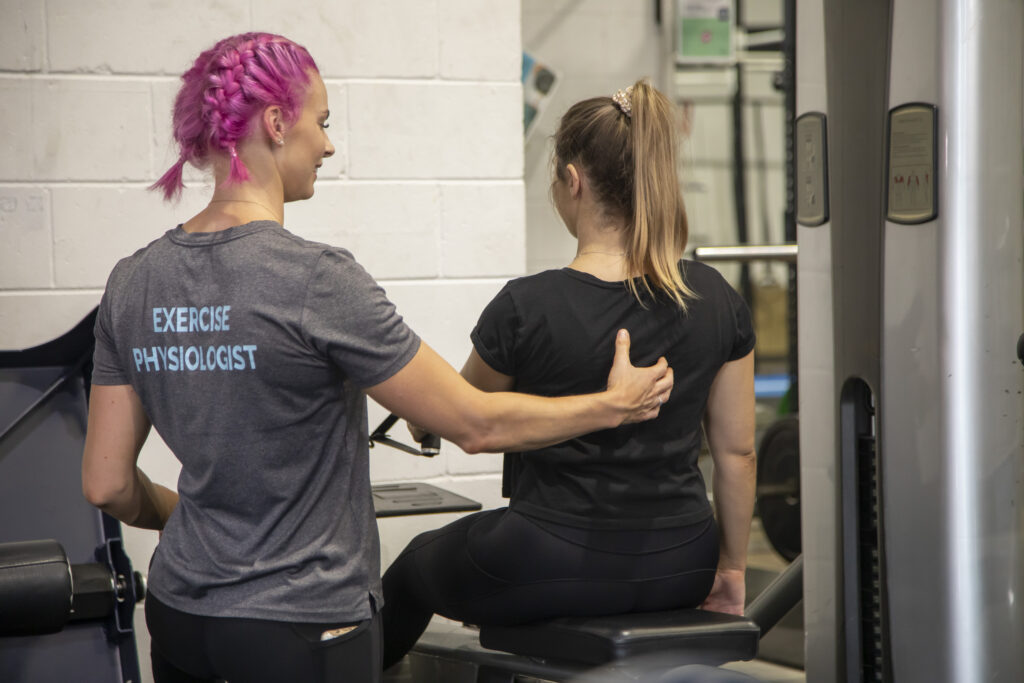
Exercise physiology focuses on the rehabilitation of musculoskeletal, neurological, cardiovascular, metabolic, respiratory, mental health, renal and oncological diseases, disorders, dysfunctions and disabilities, and injuries via exercise. Some even delve into optimising athletic performance. Physiotherapy specialises in diagnosis of musculoskeletal injuries and using hands-on methods to begin a treatment plan. By understanding the distinctions between these fields and how they complement each other, you can make informed decisions about your health and seek the right professional guidance.
Exercise Physiology
Optimising Health Through Exercise Physiology is a scientific field that examines how our bodies respond to exercise and physical activity. Its goal is to successfully help a person treat their condition until it no longer affects them, manage their condition if it is something that can’t be rehabilitated, restore the person’s quality of life, and promote overall health. Exercise physiologists mostly work with the general public with chronic health conditions, but sometimes also athletes seeking to improve their performances.

Exercise physiology brings numerous benefits to the general population. Engaging in regular physical activity can, but isn’t limited to improving cardiovascular health by reducing the risk of heart disease, lowering blood pressure, and enhancing circulation. It also aids in weight management and metabolic function, helping you maintain a healthy body weight and improve insulin sensitivity. Additionally, exercise physiology strengthens muscles, increases endurance, improves bone density, and enhances flexibility. Notably, regular exercise has a positive impact on mental well-being, reducing stress levels and improving cognitive function.
Physiotherapy
Restoring and Managing Physical Health Physiotherapy, also known as physical therapy, is a healthcare profession that focuses on the diagnosis and appropriate hands-on rehabilitating of musculoskeletal injuries and conditions. Physiotherapists utilise various techniques and interventions to alleviate pain, restore physical function, and enhance quality of life. Their expertise is applicable to individuals of all ages and physical abilities, including athletes, post-surgical patients, individuals with chronic pain, and those with mobility issues.
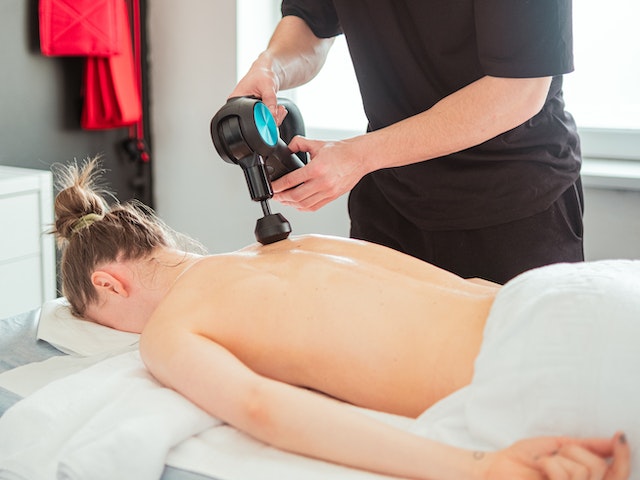

Physiotherapy aims to restore and optimise physical function, reduce pain, facilitate healing, and prevent further injuries. Physiotherapists employ different techniques tailored to individual needs. These may include manual therapy, such as joint mobilisation and soft tissue massage, exercise therapy to enhance strength, flexibility, and balance, electrotherapy to manage pain and support tissue healing, and hydrotherapy utilising water-based exercises for rehabilitation.
Differences between Exercise Physiology and Physiotherapy
While exercise physiology and physiotherapy share similarities, they differ in several aspects:
- Focus: Exercise physiology primarily studies physiological responses to exercise and develops exercise programs to optimise ideal outcomes and overall health. Physiotherapy focuses on diagnosing and treating musculoskeletal injuries and conditions, employing techniques to alleviate pain and restore physical function.
- Educational Background and Qualifications: Exercise physiologists typically hold degrees in exercise physiology, kinesiology, or related fields. They may also possess certifications from professional organisations like the Australian Strength and Conditioning Association (ASCA), American College of Sports Medicine (ACSM) or the National Strength and Conditioning Association (NSCA). Physiotherapists hold degrees in physiotherapy or physical therapy and require licensing to practise.
- Patient Population and Treatment Areas: Exercise physiologists work with a diverse range of individuals with chronic health conditions, the general public seeking general fitness improvement, and even athletes. Physiotherapists primarily focus on musculoskeletal injuries and conditions, working with athletes, post-surgical patients, individuals with chronic pain or disabilities, and those in need of physical rehabilitation.
- Collaborative Approach: Exercise physiologists and physiotherapists often collaborate to provide comprehensive care. While exercise physiologists design exercise programs specific to individual needs, physiotherapists contribute to pain management, physical techniques, and functional restoration.
How Exercise Physiology and Physiotherapy Complement Each Other

Exercise physiology and physiotherapy are interconnected fields that complement each other in promoting health and well-being:
- Role of Exercise Physiologists in Physiotherapy Settings: Exercise physiologists bring their expertise in exercise prescription, fitness assessment, and performance optimization to physiotherapy settings. They collaborate with physiotherapists to develop customised exercise programs that support rehabilitation goals and improve overall physical function.
- Incorporating Exercise Physiology Principles in Physiotherapy Interventions: Physiotherapists can integrate exercise physiology principles into treatment plans, ensuring that patients engage in appropriate and effective exercises to enhance strength, flexibility, and cardiovascular fitness. This integration can accelerate the rehabilitation process and improve long-term outcomes.
- Importance of Interdisciplinary Collaboration: The collaboration between exercise physiologists and physiotherapists underscores the significance of interdisciplinary teamwork in providing holistic care. By combining their expertise, these professionals can address a broader range of patient needs, enhance treatment outcomes, and promote long-term health and well-being.
Conclusion
Exercise physiology and physiotherapy are distinct yet interrelated fields that contribute to physical health and rehabilitation. Exercise physiology optimises athletic performance and overall health through exercise prescription, while physiotherapy specialises in rehabilitating musculoskeletal injuries. By understanding the differences between these fields and their complementary nature, you can make informed decisions about seeking the right professional guidance for your specific needs. Leveraging the expertise of exercise physiologists and physiotherapists, you can improve physical function, alleviate pain, and achieve better overall health outcomes.
References:
- American College of Sports Medicine. (n.d.). Certified Exercise Physiologist. Retrieved from https://www.acsm.org/get-stay-certified/get-certified/exercise-physiologist
- Australian Physiotherapy Association. (n.d.). What is physiotherapy? Retrieved from https://choose.physio/what-is-physiotherapy
- Canadian Physiotherapy Association. (n.d.). What is physiotherapy? Retrieved from https://physiotherapy.ca/what-is-physiotherapy
- Exercise is Medicine. (n.d.). Exercise Physiology. Retrieved from https://exerciseismedicine.org/support_page.php/exercise-physiology/
- Powers, S. K., & Howley, E. T. (2017). Exercise Physiology: Theory and Application to Fitness and Performance. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill Education.
- World Confederation for Physical Therapy. (n.d.). What is physical therapy? Retrieved from https://www.wcpt.org/what-is-physical-therapy





